Artificial Intelligence Methods for Deciphering How the Immune System Works
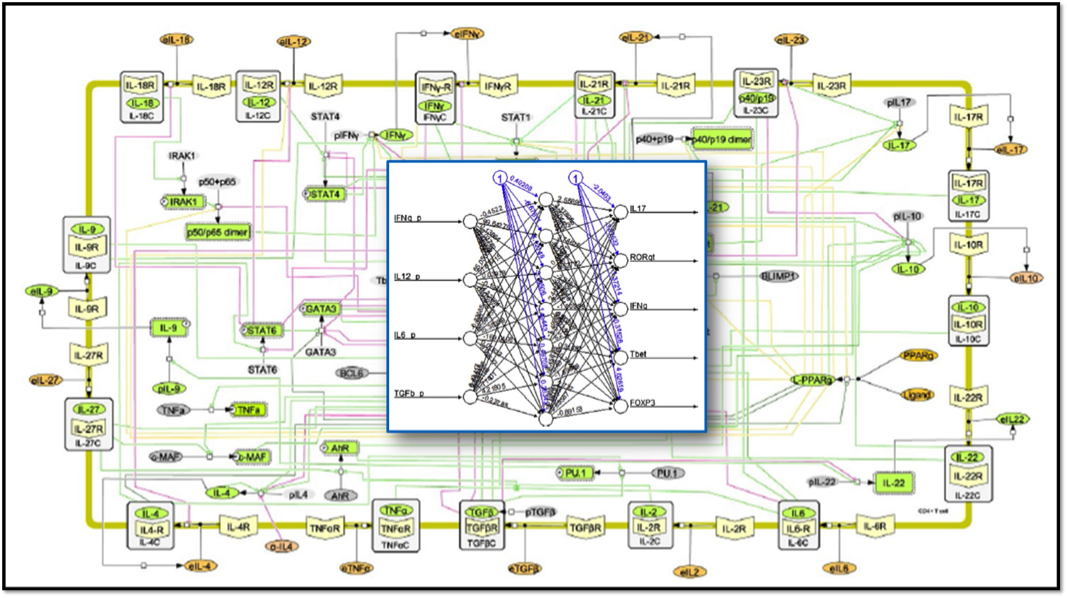
The MIEP team has successfully modeled the CD4+ T cell differentiation process by using Artificial Neural Networks (ANN). The ANN-based modeling framework is robust to noise and outperforms two other widely utilized supervised machine learning algorithms (linear regression model and support vector machine). Accordingly, ANN-based computer models of immunological networks represent ideal candidates for integration into scalable multiscale modeling platforms for massively interacting systems such as ENISI MSM that allow integration from molecular to systems and population-level spatiotemporal scales. As part of ongoing research efforts under MIEP, we have used ENISI MSM to simulate up to 107-1010 agents mapping to approximately 1% of the gut using our ENISI MSM tool.
By combining modeling and data-driven approaches along with targeted wet lab and clinical experimentation we are able to engineer information processing representations of immunological systems for advancing a systems-wide understanding of the mechanisms underlying the modulation of health outcomes. Advanced Machine Learning and Big Data Analytics have significantly expedited and transformed immunoinformatics research at VBI.
About NIMML
The NIMML Institute is a 501 (c) (3) non-profit public charity foundation focused on a transdisciplinary, team-science approach to precision medicine at the interface of immunology, inflammation, and metabolism. The NIMML Institute team has led numerous large-scale transdisciplinary projects and is dedicated to solving important societal problems by combining the expertise of immunologists, computational biologists, toxicologists, modelers, translational researchers, and molecular biologists. The Institute is headquartered in Blacksburg, VA. For more information, please visit www.nimml.org or contact pio@nimml.org.
